
Backup Rings and Their Importance to High-Pressure Aerospace Hydraulic Systems
Posted by CDI Products on Nov 14, 2023
High-pressure aerospace hydraulic systems power everything from an aircraft's landing gear, flight controls, fuel systems and brakes. These intricate systems work harmoniously to ensure the aircraft's safe and efficient operation. Yet, they can't function optimally without a component that's often overlooked but undeniably crucial – the backup ring.
Backup rings may be trivial, but their impact is mighty. They play a vital role in preserving the integrity of seals within pressurized aerospace hydraulic systems, minimizing leakage, and extending the lifespan of the components they protect. Let's explore the importance of a backup ring, their types, and why they are critical for these hydraulic systems.
What are Backup Rings?
A Backup ring is rigid ring typically made from thermoplastic material like virgin or filled PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), or high-performance thermoplastic such as PEEK (Polyether ether ketone). These rings are designed to close off the sealing system's extrusion gap and support the primary seal, especially under high-pressure conditions.
They are typically used in conjunction with O-rings, where they prevent extrusion - the phenomenon where a seal deforms under high pressure and moves into the clearance gap, leading to seal damage and system failure. The backup ring adds support and durability, ensuring the seal remains in its intended shape and place.
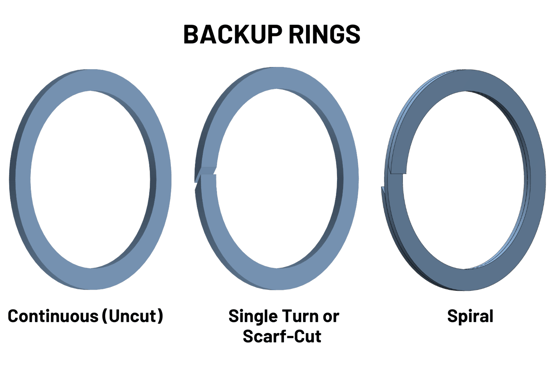
Types of Backup Rings with Advantages & Disadvantages
There are mainly three types of backup rings: Continuous (also known as uncut or solid), Single Turn (also known as scarf-cut or cut), and Spiral.
Continuous (Uncut or Solid) Backup Rings: The continuous uncut backup rings provide the most reliable anti-extrusion protection for seals. Since they are a continuous structure, their extrusion protection is not impacted by temperature changes, which cause material movement (expansion and contraction) in the scarf cut portion of the Backup Ring.
Advantages -
- Can be used for large diameters without the risk of the ring opening due to temperature variations.
- Ease of assembly onto the hardware without the risk of chafing the ends of the backup ring (no ends).
- Can be used in applications with linear, rotary or helical movements.
- Very good extrusion protection at high pressure and impulse pressure.
Disadvantages -
- Pressure trapping between the o-ring and backup ring can occur and cause increased friction.
- High pressure, dynamic used with O-Rings is not recommended. Additional validation testing and consideration in material selection is recommended.
- Some cross sections, typically the smaller dash numbers may be difficult to install into closed glands.
Single Turn (Scarf-Cut or Cut) Backup Rings: Single Turn or Scarf-Cut Backup Rings are distinguished by their angled or "scarf" cut. This cut allows the ring to be opened and fitted over a shaft or into a housing without the assistance of installation and resizing tools. Because of their design and the temperature impact on material movement, it is recommended to investigate and determined if there is sufficient support in the scarf cut region of the Backup Ring to provide adequate extrusion protection at the temperature extremes of your application.
Advantages -
- The installation in the gland is easier due to the scarf-cut.
- Scarf-cut ring prevents pressure trapping.
- May be installed even for very small rods, less than ½” inch (12.7 mm), but necessary care should be taken to ensure correct installation.
Disadvantages -
- Cut will “open up” at low temperature due to the contraction of the ring. However, the AS5781 and AS5860 sizes are safe for use in a wide temperature range, from -67 °F to +275 °F (-55 °C to +135 °C) and the scarf-cut has been designed to maintain a minimum 50% overlap. Note that some larger sizes are designed to overlap at ambient temperature in order to maintain the minimum 50% overlap at -67 °F (-55 °C). Backup rings should not be trimmed to size upon installation.
- Do not use in applications with rotary or helical movements, as the scarf-cut may separate/overlap due to the movement and the backup ring may attempt to “wind” out of the gland.
- If possible, avoid use in “screw in” applications, as the scarf -cut may separate/overlap due to the movement.
- Ends of backup rings may be caught and cut/damaged during assembly of piston into the bore or rod into the housing.
- Scarf-cut may cause erosion of the O-Ring during impulse press situations and at high pressure, particularly when using a higher filled PTFE materials which tends to be harder.
- Scarf-cut ends may extrude into the gap between the piston/cylinder or rod/gland during the impulse pressure situations and at high pressure.
Spiral Backup Rings: The use of spiral-cut backups is not recommended for new designs due to many disadvantages. They have almost all the disadvantages of the continuous (solid) and single turn (scarf-cut) backup rings. Additionally, since the spiral-cut ring has two coils, each with only 50% of the width of the continuous and single turn rings, they have poor extrusion resistance. The only advantages they do offer are that they will never present a gap (as opposed to the single turn ring) and an oversized ring may be sized, cut, and used in the field for a non-standard or smaller size, which is not a recommended practice. Installation into the gland of these rings is simple, but the thin ends of the ring may easily be cut by the hardware during assembly of the unit, and screwing a gland into the hardware presents a more severe problem than that of single turn rings.
The Significance of Backup Rings
The aerospace industry demands systems that operate effectively and reliably under extreme conditions, including temperature variations and high pressures. This is precisely where backup rings prove their worth. Here are the four reasons why they are vital for high-pressure aerospace hydraulic systems:
- Seal Support and Protection:Backup rings significantly reduce the chances of seal extrusion, especially under high-pressure conditions. This protection ensures the seal remains effective, minimizing potential leaks that could compromise the system's performance.
- Enhanced Component Lifespan:By providing necessary support, backup rings help extend the seals' lifespan, increasing the service life of the hydraulic system components. This translates to reduced maintenance requirements and operational costs.
- System Reliability:Backup rings enhance the reliability of hydraulic systems, ensuring they function optimally even under the extreme conditions encountered in aerospace applications. This reliability is critical for ensuring safety and operational effectiveness.
- Compatibility with Various Fluids:Backup rings are made from thermoplastic materials which are resistant to aerospace fluids, making them suitable for various applications within the industry.
Backup rings might not be the most prominent or conspicuous components within a hydraulic system, but their role is undeniably crucial. These components play a substantial role in enhancing system reliability and longevity.
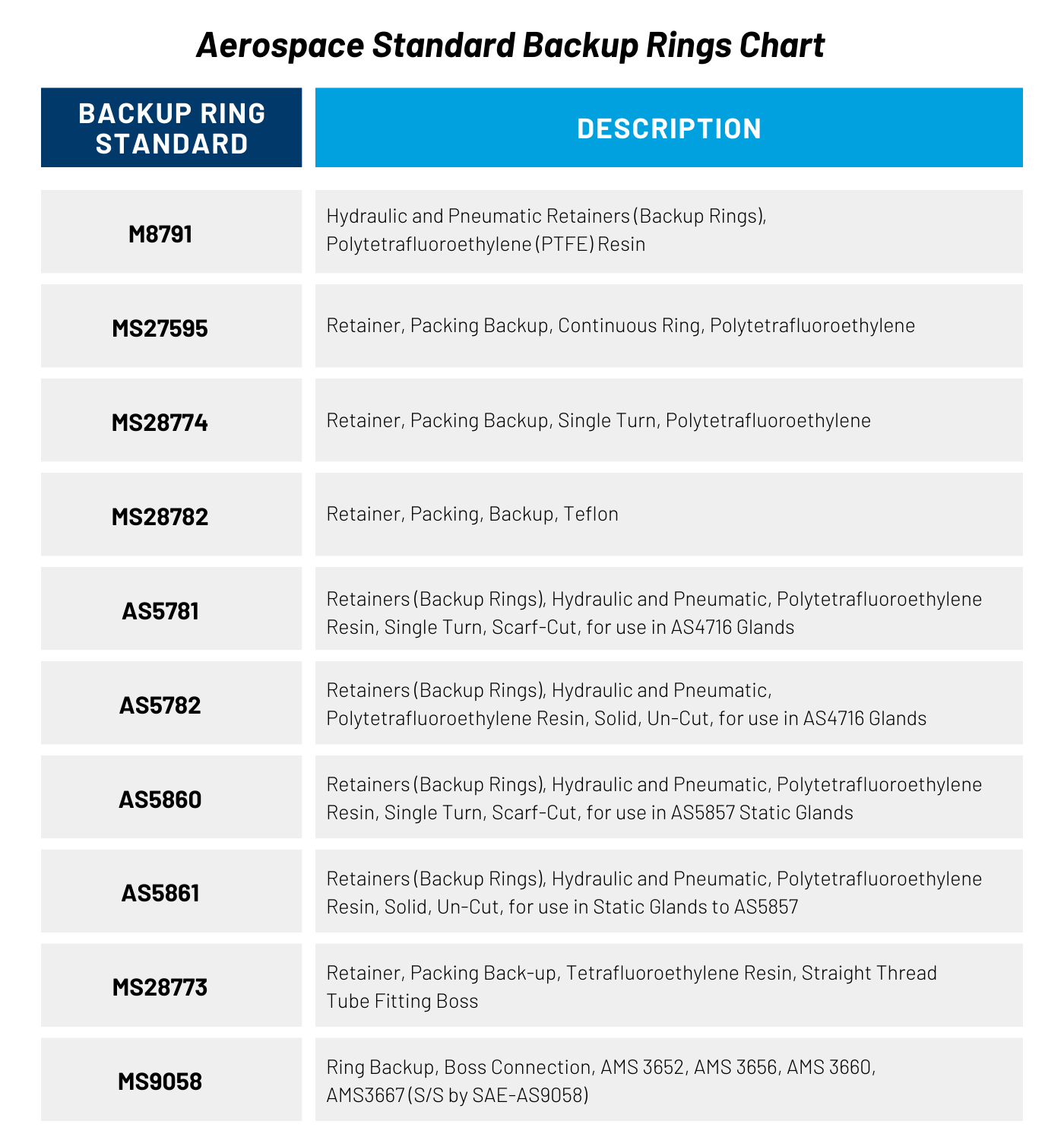
Topic: aerospace, PTFE, high pressure, backup rings, types of back up rings
